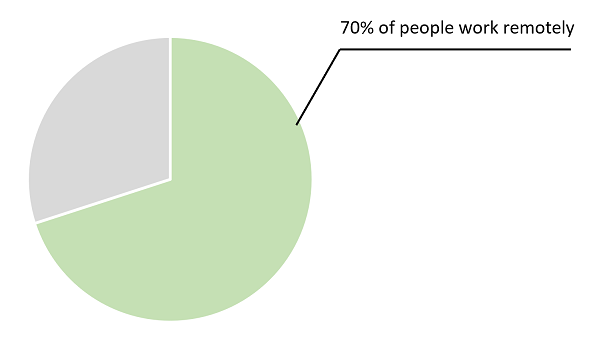
Work from Home (WFH) policies have been proliferating throughout organizations. Today. 70% of people, globally, work remotely at least once a week, and 53% work remotely for at least half of the week. However, with COVID-19 not ceasing, it is becoming more common for employees to work out of office; and this trend is likely here to stay. WFH brings about benefits to both the employee and employer in the form of greater flexibility, increased productivity and, as a result, higher profits.
However, with these benefits come perilous risks. The increased use by bad actors of Rogue Devices (manipulated hardware that acts with malicious intent) is being facilitated by these WFH policies since there are more entry points and fewer security measures in place (as, often, WFH is associated with BYOD).
Spoofed Peripherals and Network Implants have the ability to carry out various forms of attacks, including malware dissemination, data breaches, man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks, network sniffing, and more. The consequences of an attack can be substantial and are often made up of financial, reputational and legal costs, something that any organization wants to avoid.
Besides carrying out noxious attacks, Rogue Devices are almost impossible to detect, thus making them extremely threatening. Spoofed Peripherals are recognized as legitimate HIDs and Network Implants. They can go completely undetected as they operate on Layer 1 – the Physical Layer – which is not covered by existing security software solutions. As such, Rogue Devices do not raise any alarms.
What are the risks?
Data
Working remotely requires information to be shared. When employees are working on a public Wi-Fi hotspot, the information is being disseminated over an unsecured network.
Remote Desktop Access is a common feature of remote work, and this can be risky too. Even if the individual is working on a secure, private network, those people\devices he is sharing the desktop with (which contains sensitive information) might not be protected enough, and the router to which those devices are connected to might have been compromised.
Data is the most important aspect that should be taking into account while working remotely as it means malicious actors can cause damage to an organization without ever gaining physical access to its premises.
Insufficient Security
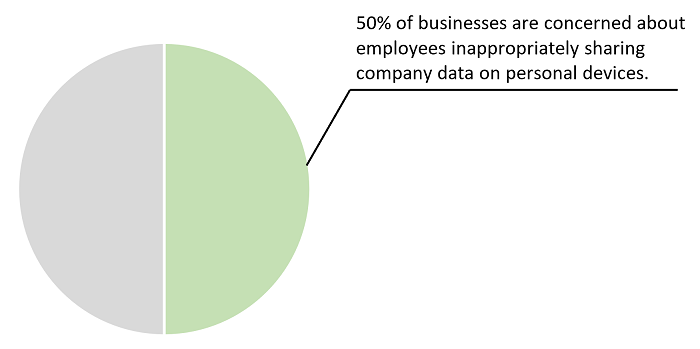
Since WFH often means using personal devices for work purposes, these personal devices are becoming appealing attack targets due to their lack of sufficient security measures. 50% of companies that permitted BYOD were breached by an employee-owned device. Without adequate security features, careless actions by employees are more difficult to prevent. As such, around 50% of businesses worldwide are concerned about employees inappropriately sharing company data via the personal devices they use for work purposes.
Employee Action
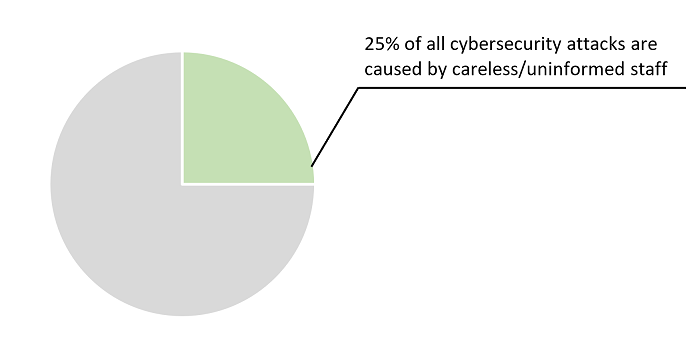
Careless/uninformed staff cause a quarter of all cybersecurity attacks, and working remotely only increases the chances of this happening. Employees can be oblivious to what is being connected to their devices. Moreover, connecting to a public Wi-Fi hotspot is common when working remotely, yet highly risky as the router might have been compromised with a Network Implant, thus allowing the perpetrator to gain remote access to, and manipulate the data on the network and connected devices.
Malicious employees pose a grave danger to organizations, especially when working remotely as there are no prying eyes to catch them out. These ill-intentioned employees might make use of a Rogue Device to carry out their attack.
Ways to lower the risk
1) Remote Work Policy
The first thing that needs to be done is to create a Remote Work Policy that clearly defines how employees can work remotely; whether that means tweaking the BYOD policy, or requiring employees to use company-issued devices only, in addition to determining the extent to which staff can carry out their jobs with minimal restrictions if any. The Remote Work Policy should be approved by a range of stakeholders to ensure it is based on the interests of all parties involved with the company to certify efficiency. The following risk-reducing procedures might be included in the provisions of the Policy.
2) Principle of Least Privilege
This gives employees access to only the data they need to perform their job, thereby reducing the amount of data accessible from employees’ devices. Since the exposure of data is one of the greatest risks when working remotely, the Principle of Least Privilege reduces the amount of data being purloined, should an attack take place.
3) Zero Trust Network Access
Based on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” ZTNA ensures that trust is not automatically given. Access should be granted on a “need-to-know,” least-privileged basis, defined by meticulously created policies. ZTNA, as such, recognizes that trust is a vulnerability and therefore prevents lateral movements; the prime technique used by malicious actors as their point of access is usually not their actual target. ZTNA therefore complicates and incommodes the attack.
4) Virtual Private Network
VPNs create encrypted tunnels between a user’s device and the Internet. Employees can access their files remotely without being “watched” as no-one between the user and the server they are connecting to can gain access to the data that is being transmitted, thus providing greater protection from network implants. VPNs are crucial when working remotely as, when connecting to a public Wi-Fi network, one can never be sure who set it up or who else is connecting to it.
5) Staff Education and Training
One of the most vital ways to reduce cyber risks is to enhance employee’s education and training on the topic. Social engineering, for example, can only be prevented by increased training and awareness. Organizations need to stress the risks of connecting peripherals to their devices and make them suspicious of where the peripheral is coming from. Peripherals should always be bought from reputable sources such as Apple. Carrying a portable charger when working in locations other than one’s home will ensure that employees are using a trusted peripheral. Furthermore, employees should know not to let others use the device they use for work purposes.
6) Rogue Device Mitigation Software
The best way to reduce the risk of Rogue Device attacks is to implement a Rogue Device Mitigation software that can detect such attack tools and take action to prevent their success. Sepio Systems offers such software that protects both the endpoint and the network.
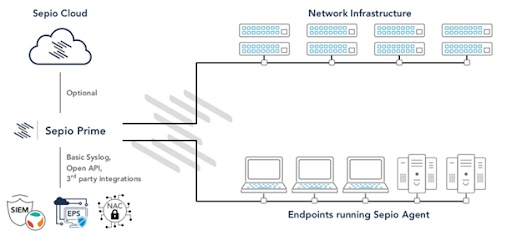
Sepio Systems Solutions
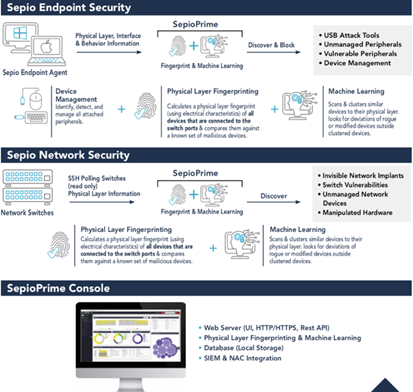
Sepio Systems is the leader in the Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM) market and is disrupting the cybersecurity industry by uncovering hidden hardware attacks. As the only security solution for Physical Layer attacks, Sepio Prime provides security teams with full visibility into their hardware assets and their behavior in real-time. A comprehensive policy enforcement module allows administrators to easily define granular device usage rules and continuously monitor and protect their infrastructure. Leveraging a combination of physical fingerprinting technology together with device behavior analytics, Sepio’s software-only solution offers instant detection and response to any threat or breach attempt coming from a manipulated or infected element.